- Docs
- /
SQL Server Authentication
13 Mar 2021 22676 views 0 minutes to read Contributors ![]()
Introduction
Authentication means a process of identifying a user or a person based on their username and password.
SQL Server also authenticates their users by their credentials.
SQL Server uses the following 2 types of authentication.
- Windows Authentication.
- SQL Server Authentication.
Windows Authentication
In Windows Authentication mode, when you're using SQL Server from the same computer as where it's installed, SQL Server doesn't ask for username and password as shown below.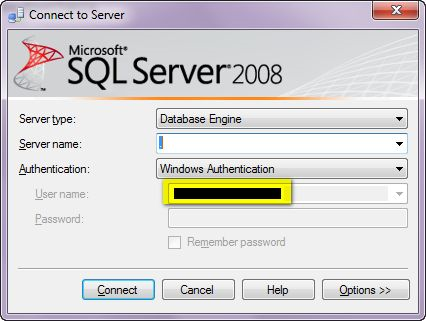
As you can see, in Windows Authentication mode, the username and password fields are disabled. SQL Server uses your computer's username as the SQL Server username. And when you click on the connect button, it'll provide you the access.
Because SQL knows that the user is already logged into the operating system with the correct credentials and it allows user to access databases.
SQL Server Authentication
When you use SQL Server Authentication, you must require a username and password. In the business world, most applications use this authentication to provide their client or vendor access to their databases.
An instance of SQL Server can have multiple user accounts with various usernames and passwords. In a shared environment, since different users have different access on different databases, SQL Server Authentication should be used.
The following is an example of that.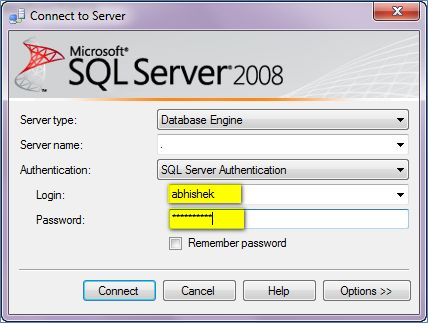
When a user connects with a specified login name and password from a non-trusted connection, SQL Server does the authentication itself by checking to see if a SQL Server login account has been set up and if the specified password matches the one previously recorded.
If SQL Server does not have a login account set, the authentication fails and the user receives an error message as shown below.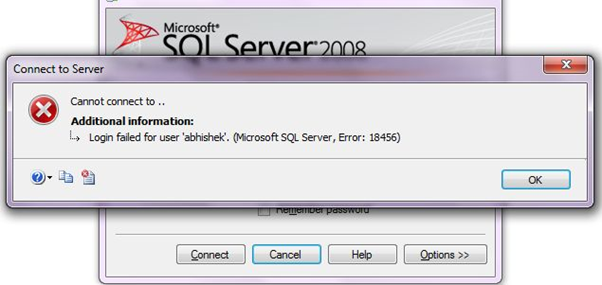
SQL Server Authentication is provided for backward compatibility because applications written for SQL Server version 7.0 or earlier may require the use of SQL Server logins and passwords.
Additionally, SQL Server Authentication is required when an instance of SQL Server is running on Windows 98 because Windows Authentication Mode is not supported on Windows 98.
The following is the flowchart for the process of authentication.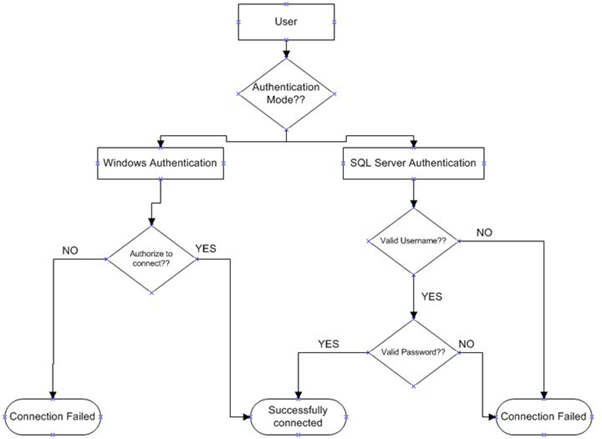
As you can see, when the user tries to connect to SQL Server, SQL Server asks the user for the mode of authentication. If the user selects “Windows Authentication” then SQL Server checks whether the user is authorized to connect. If yes then it'll open the gate for the user to access the data else it throws an error.
If the user chooses the second option, in other words “SQL Server Authentication”, then SQL Server asks for username and password.
Next when the user enters his/her credentials, SQL Server checks the entered credentials with the credentials stored in the master database. If both credentials matche then it allows the user to connect to SQL Server else it'll give an error.
So, these are the ways by which we can connect to SQL Server.
In this article

